-
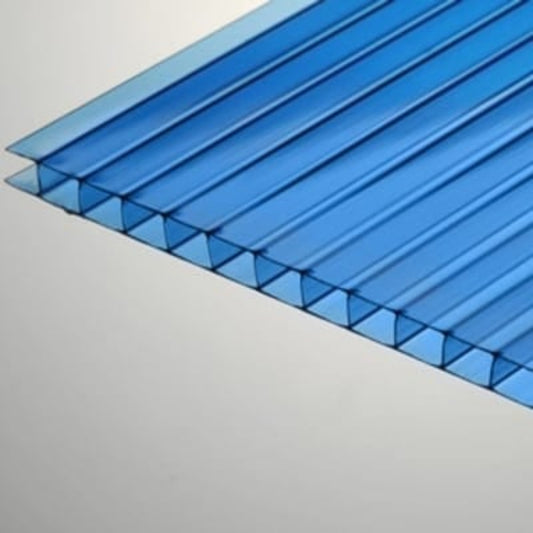
Twinwall Polycarbonate Sheet - All Sizes
Vendor:Roofing4US PolycarbonatefromRegular price $41.78Sale price $41.78 Regular priceUnit price per
Greenhouse Plastic Sheets | Greenhouse Panels | Acrylic | Greenhouses | Plastic
Welcome to the Greenhouse Plastic Sheets section of Roofing4US. This category is dedicated to providing gardeners and greenhouse enthusiasts with the highest quality plastic sheets tailored for greenhouse applications. Each sheet type in our collection has been selected for its durability, light transmission properties, and resistance to extreme weather conditions. Let’s explore the general categories of sheets available and their best use cases.
Types of Greenhouse Plastic Sheets
Clear Hammered Sheets
Clear Hammered Sheets, as the name suggests, feature a unique hammered texture. These sheets scatter sunlight in diverse angles, thus offering a more diffused lighting inside the greenhouse. This diffused light can reduce the risk of plants getting burned by direct sunlight.
Practical Uses: Perfect for greenhouses where plants require indirect sunlight. This type of sheet is also aesthetically pleasing due to its textured surface.
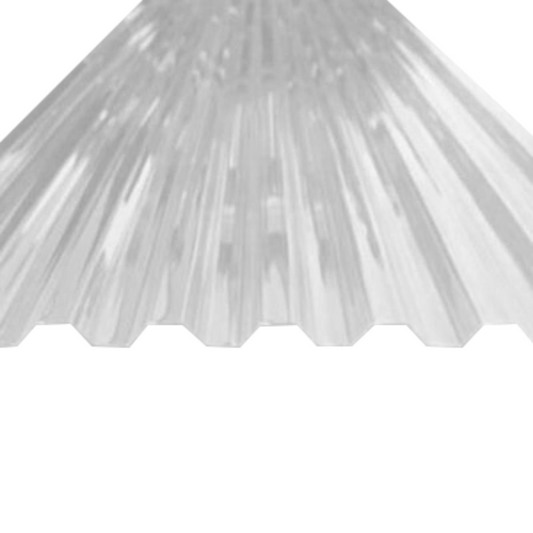
Greca Polycarbonate Corrugated Clear Roofing Sheets
Crafted from robust polycarbonate material, these sheets offer the classic corrugated design. They are renowned for their strength and ability to disperse light evenly throughout the greenhouse.
Practical Uses: Suitable for larger greenhouses or those in regions with unpredictable weather. The corrugated design not only provides strength but also helps in channeling rainwater away efficiently.
Multiwall Polycarbonate Sheets
These sheets are characterized by multiple walls or layers, making them one of the most insulated options available. They offer excellent thermal properties, ensuring that the greenhouse remains warm even during colder months.
Practical Uses: Ideal for areas with harsh winters or for gardeners aiming to grow tropical plants in cooler regions.
Twinwall Polycarbonate Sheets
A subset of multiwall sheets, Twinwall Polycarbonate Sheets consist of two layers, offering a balance between insulation and light transmission. They're lighter than the multiwall sheets, making them easier to handle and install.
Practical Uses: Suitable for both new and existing greenhouses, especially if you're looking for a compromise between weight, insulation, and price.
Guidance on Selection
Size & Dimensions: Ensure that you measure the size of your greenhouse accurately before choosing the sheets. All the products come in various widths and lengths, catering to diverse needs.
Weather Conditions: Depending on the climatic conditions of your region, select a sheet that offers optimal insulation (for colder regions) or UV protection (for sunnier regions).
Plant Requirements: Some plants prefer indirect or diffused light, while others might thrive under direct light. Select a sheet that complements the needs of your plants.
Budget: While all our sheets are competitively priced, the costs vary based on the material and design. Make a choice that aligns with your budget without compromising on the quality.
Greenhouse Plastic Sheets
Greenhouse plastic sheets are essential elements within contemporary greenhouse structures. They serve to cover the framework of the greenhouse, establishing an enclosed space that allows for precise control over temperature, humidity, and light levels. These sheets are crafted from diverse plastic materials, with polyethylene being the most prevalent due to its cost-effectiveness, durability, and efficient light diffusion properties.
Key attributes of greenhouse plastic sheets encompass:
Light Passage: Greenhouse plastic sheets are specifically designed to enable sunlight to enter while scattering it, mitigating the risk of harsh direct light that could harm plants. This promotes an ideal environment for plant growth.
UV Safeguard: High-quality greenhouse plastic sheets are often treated to block detrimental ultraviolet (UV) rays, safeguarding plants and reducing plastic degradation.
Resilience: Premium sheets are resistant to tears, punctures, and deterioration caused by exposure to weather conditions. They're engineered to endure extreme temperatures, wind, and other environmental factors.
Thermal Efficiency: These sheets effectively retain heat within the greenhouse, establishing a warmer climate that extends the growing season and shields plants from cold weather.
Variation: Greenhouse plastic sheets are available in different thicknesses and diffusion levels. Thicker sheets provide better insulation and longevity, while varying degrees of light diffusion cater to different plant types.
Anti-Condensation Qualities: Certain greenhouse plastics are designed to minimize condensation formation on their inner surface. This helps maintain optimal humidity levels and prevents water droplets from falling onto plants.
When selecting greenhouse plastic sheets, it's important to take into account factors such as your region's climate, the specific plant varieties you intend to cultivate, and your budget. Proper installation and upkeep also play a pivotal role in maximizing the advantages of greenhouse plastic sheets.
Regular cleaning to eliminate dust and dirt accumulation, as well as periodic inspections to detect signs of wear and tear, are critical to ensuring the durability and efficacy of the plastic sheets.
Overall, greenhouse plastic sheets are fundamental components of contemporary greenhouse technology, enabling efficient and controlled plant cultivation across various climates and settings.
Different types of greenhouse
Certainly, here are descriptions of various greenhouse types:
Lean-To Greenhouse
A lean-to greenhouse is constructed alongside an existing structure like a house or building. It shares a wall with the supporting structure and often features a slanted roof. This kind of greenhouse is useful in compact spaces and provides convenient access to utilities from the connected building.
Freestanding Greenhouse
A freestanding greenhouse is an independent structure that stands on its own without being connected to any other building. It can be situated anywhere on your property, offering flexibility in terms of size and design.
Gable Greenhouse
This type of greenhouse boasts a traditional peaked roof resembling that of a house. It offers ample vertical room for tall plants and efficient runoff of rain and snow. Gable greenhouses generally offer a spacious and well-ventilated environment.
Dome Greenhouse
Dome greenhouses possess a curved roof resembling a dome shape. They catch the eye with their distinctive appearance and ensure effective airflow, aiding in regulating temperature and humidity.
Quonset Greenhouse
Quonset greenhouses showcase a semicircular or hoop-shaped roof constructed from curved metal pipes or tubes. They are relatively simple to construct, cost-effective, and offer solid resistance against wind and snow loads.
Sawtooth Greenhouse
Sawtooth greenhouses feature a unique roof design with multiple ridges and valleys, resembling the teeth of a saw. This design optimizes exposure to natural light, making it a suitable choice for commercial operations.
A-Frame Greenhouse
Similar to the gable style, an A-frame greenhouse has a steeply sloped roof forming an "A" shape. This structure provides abundant vertical space and efficient water drainage.
Ridge-and-Furrow Greenhouse
In this type, several interconnected greenhouse sections share a central ridge. The planting areas are in the furrows between the ridges. This layout is efficient for large-scale commercial production.
Window-Mounted Greenhouse
These are compact greenhouse units that can be attached to windows or walls. They're ideal for starting seedlings or cultivating herbs and small plants.
Polytunnel Greenhouse
Also recognized as hoop houses, polytunnel greenhouses consist of a series of arched ribs covered with plastic. They offer a cost-effective method to extend the growing season and safeguard plants from the elements.
Each greenhouse type presents its own advantages and constraints, and the selection hinges on factors such as available space, climate, intended purpose, and personal preferences.
What are advantages of a greenhouse?
The benefits of utilizing a greenhouse:
Extended Planting Duration: Greenhouses facilitate a longer span for planting, exceeding the confines of outdoor conditions. This enables an earlier commencement in spring and later harvesting in autumn, or even continual production, contingent on your local climate.
Temperature Regulation: Greenhouses offer the ability to manage temperatures. This proves especially useful for shielding plants from frost, extreme cold, or excessive heat. You can establish the ideal temperature range to foster optimal plant growth.
Weather Shielding: Greenhouses provide a shield against harsh weather elements like heavy rainfall, wind, hail, and snow. This defense curtails physical harm and the potential transmission of diseases, contributing to healthier plant life.
Pest and Disease Management: The enclosed environment of a greenhouse acts as a barrier against many pests and diseases. This diminishes the need for extensive chemical interventions, fostering a healthier ecosystem for plant growth.
Controlled Humidity: Greenhouses offer control over humidity levels, essential for the well-being of numerous plant species. This proves particularly advantageous for tropical plants that necessitate higher humidity levels than those offered by your local climate.
Managed Light Exposure: Greenhouse coverings can scatter sunlight, reducing the risk of sunburn on delicate plants. Additionally, you can manipulate light exposure through shading methods, safeguarding plants from excessive light and heat.
Accelerated Plant Development: The controlled setting within a greenhouse often results in swifter and more robust plant growth. Customized conditions ensure increased yields and healthier vegetation.
Efficient Water Utilization: Greenhouses curtail water wastage by minimizing evaporation within the enclosed space. Controlled irrigation systems further ensure plants receive the appropriate amount of water, reducing the chances of under or over-watering.
Tailored Soil Conditions: Greenhouses offer the flexibility to establish and maintain specific soil conditions tailored to plant requirements. This involves adjustments in pH levels, nutrient content, and soil composition.
Year-Round Plant Diversity: Greenhouses enable the cultivation of diverse plant species that may not be indigenous to your locale or struggle in the local climate. This diversity provides opportunities for exploration and specialized crops.
Enhanced Crop Quality: The controlled environment within greenhouses can yield superior quality produce. Consistent conditions result in uniform sizes, colors, and flavors in fruits and vegetables.
What color plastic is best for greenhouse?
The decision regarding the ideal plastic color for a greenhouse relies on the specific requirements of the cultivated plants and the local climate. In general, greenhouse plastics are available in clear, white, and occasionally other hues like green. Here's some information about each color:
Transparent Plastic: Clear plastic permits the maximum sunlight penetration into the greenhouse. This is particularly advantageous during colder seasons when optimizing solar heat intake is vital for sustaining temperatures. It suits crops that demand elevated light levels and is commonly employed in regions with cooler weather.
White Plastic: White plastic reflects a significant portion of sunlight, diminishing heat buildup within the greenhouse. This helps avert overheating during hot summers or in areas with intense sun exposure. White plastic also offers a more diffused light setting, which can be advantageous for light-sensitive plants or those requiring uniform light distribution. Nonetheless, it might slightly decrease total light levels compared to clear plastic.
Green Plastic: Green plastic is less prevalent but is occasionally used. It filters sunlight and provides diffused light, similar to white plastic. Green plastic can establish an environment suitable for plants sensitive to shading, although it might lead to lower overall light levels compared to clear plastic.
In the end, the choice of plastic color hinges on the particular needs of your plants and the prevalent weather conditions in your vicinity. Some growers even combine clear and shading materials to strike a balance between light transmission and heat reduction.
What is greenhouse plastic?
Greenhouse plastic refers to a specialized type of plastic sheet or film that is designed for covering the framework of a greenhouse structure. Its purpose is to enclose the interior space of the greenhouse, creating a controlled setting for plant growth. This plastic is a vital component of modern greenhouse technology, capable of regulating factors such as light, temperature, and humidity within the enclosed area.
Usually crafted from polyethylene, a durable and versatile polymer, greenhouse plastic sheets come in various thicknesses and may possess features like UV resistance and light diffusion properties.
Key attributes of greenhouse plastic encompass:
Light Passage: Greenhouse plastic is formulated to allow sunlight to enter while often diffusing it to prevent intense direct exposure that could harm plants.
UV Shielding: Many types of greenhouse plastic are treated to block harmful ultraviolet (UV) rays, safeguarding both the plastic itself from degradation and the plants inside from potential UV-related harm.
Robustness: High-quality greenhouse plastic is engineered to endure outdoor challenges, including wind, rain, snow, and temperature fluctuations.
Heat Retention: Greenhouse plastic aids in retaining warmth within the structure, establishing a warmer climate that extends the growing season and guards plants against cold conditions.
Light Scattering: Certain greenhouse plastics are designed to scatter and distribute sunlight, creating more uniform light dispersion throughout the greenhouse.
Prevention of Condensation: Specific greenhouse plastics are designed to reduce the formation of condensation on the inner surface, assisting in maintaining ideal humidity levels.
Control of Infrared Radiation: Advanced greenhouse plastics can even manage the emission of infrared radiation, contributing to a more stable internal temperature.
Typically installed by stretching it over the greenhouse framework and securing it, greenhouse plastic plays a pivotal role in crafting an environment where cultivators can have heightened control over growth conditions. This leads to healthier plants, increased yields, and an extended period for cultivation.
Which type of plastic is used in the greenhouse?
The type of plastic frequently utilized in greenhouses is polyethylene. Polyethylene is a versatile polymer well-suited for greenhouse applications. Its characteristics make it a suitable choice for establishing a controlled environment within a greenhouse. This plastic is selected for its durability, cost-effectiveness, and its ability to permit light passage while effectively scattering it, which is advantageous for optimal plant growth.
Polyethylene plastic used in greenhouses is often treated to incorporate additional features like UV protection, aiding in shielding against the harmful effects of ultraviolet rays and increasing its longevity when exposed to sunlight. It is accessible in various thicknesses, each offering different levels of insulation and sturdiness.
Polyethylene plastic is recognized for its resistance to tearing, puncturing, and other environmental pressures, making it a pragmatic option for safeguarding plants and upholding a stable growing environment. Its adaptability, widespread availability, and economical nature establish it as a favored choice for greenhouse coverings.
Here are several key benefits associated with using polyethylene in greenhouse contexts:
Light Permeability: Polyethylene facilitates sunlight penetration, supporting photosynthesis and fostering robust plant growth. Its design effectively scatters light, minimizing the risk of intense direct light that could potentially harm plants.
Cost-Effective: Polyethylene represents a cost-efficient solution for greenhouse coverings. It delivers the necessary functionality without incurring exorbitant costs, rendering it a pragmatic choice for both individual and commercial greenhouse operations.
Durability: This plastic variant is engineered to withstand diverse weather conditions, including wind, rain, and fluctuations in temperature. It resists tearing and punctures, providing plant protection and upholding the structural integrity of the greenhouse.
UV Shielding: Many polyethylene films undergo treatment to block detrimental ultraviolet (UV) rays. This safeguards both the plastic itself from UV-induced degradation and the plants within from potential UV-related harm.
Thermal Efficiency: Polyethylene aids in retaining warmth within the greenhouse, extending the growing season and shielding plants from cold external temperatures. It establishes a microclimate more conducive to plant development than the open environment.
Ease of Setup: Polyethylene sheets are relatively straightforward to install over the greenhouse framework. They can be stretched and secured in position, creating a snug and effective enclosure.
Adaptability: Polyethylene is available in diverse thicknesses, allowing growers to select the appropriate level of insulation and sturdiness based on their specific requirements and local climatic conditions.
Repair and Replacement: In the event of damage, polyethylene sheets are comparatively easy to replace or mend, minimizing downtime and costs when compared to more intricate greenhouse coverings.
In summary, polyethylene plastic presents a harmonious blend of affordability, durability, and functionality, rendering it a favored choice for greenhouse coverings. It facilitates controlled plant cultivation while affording protection against external elements, contributing to healthier and more productive crop yields.
What precautions should be taken when choosing greenhouse plastic for the greenhouse?
When deciding on greenhouse plastic for your greenhouse, there are several precautions you should keep in mind to ensure the right choice for your specific requirements. Here's a paraphrased list of precautions to consider:
UV Resistance: When selecting greenhouse plastic, prioritize UV-resistant options. Sunlight's UV rays can degrade plastic over time, causing reduced durability and potential brittleness. Plastic with UV protection additives guards against this deterioration.
Quality: Opt for high-quality greenhouse plastic. Cheaper alternatives may lack the same level of durability and features as better-quality plastics. Investing in superior plastic can ultimately save you money by delivering improved performance and longer life.
Light Diffusion: Think about whether you need plastic with light-diffusing properties. Light-diffusing plastic scatters sunlight, preventing concentrated heat spots and shadows in the greenhouse. This results in a more uniform light distribution for your plants.
Thickness: Choose the appropriate plastic thickness. Thicker plastic provides better insulation and durability, while thinner options might suit shorter-term projects or milder climates.
Climate Considerations: Factor in your local climate. If you're in a region with strong sunlight, make sure the plastic offers sufficient UV protection. For areas prone to heavy snow or strong winds, opt for thicker and sturdier plastic.
Durability: Seek plastic that is tear-resistant and can withstand potential damage from wind, hail, or other weather conditions. This is crucial to maintain the structural integrity of the greenhouse.
Warranty: Confirm if the greenhouse plastic comes with a warranty. A reputable manufacturer should stand behind the quality and durability of their product.
Light Transmission: Consider the plastic's light transmission characteristics. Some plants require specific light levels for optimal growth, so select plastic that aligns with your crops' light needs.
Ease of Installation: Evaluate how easy the plastic is to install. Some plastics might be simpler to stretch and secure over the greenhouse frame, saving you time and effort during setup.
Anti-Condensation Properties: If you're concerned about interior condensation, look for plastic options that offer anti-condensation properties.
Longevity: Think about the expected lifespan of the plastic. Good-quality greenhouse plastic should remain effective and robust for several years, allowing you to maximize your investment.
Manufacturer Reputation: Choose plastic from established manufacturers or suppliers. Research reviews and recommendations to ensure you're getting a reliable product.
By observing these precautions, you can make an educated decision when selecting greenhouse plastic, ensuring your greenhouse is equipped with an appropriate covering that creates ideal conditions for your plants' growth and protection.
Which is the most durable plastic for greenhouse?
Polycarbonate is often regarded as one of the most robust plastic options for greenhouse use. Polycarbonate sheets are recognized for their exceptional strength, resistance to impacts, and extended lifespan. They can endure challenging weather conditions, including heavy snow, hail, and strong winds, making them a favored selection for greenhouses located in regions with demanding climates.
Polycarbonate's durability stems from its unique composition and production process. This thermoplastic polymer is known for its remarkable resistance to impacts and its ability to maintain its structural integrity even when subjected to stress. Polycarbonate sheets are nearly unbreakable, providing elevated protection for both plants and the greenhouse framework itself.
In addition to their durability, polycarbonate sheets also offer excellent light transmission while diffusing sunlight to prevent concentrated heat spots and shadows within the greenhouse. This contributes to an even dispersion of light, which benefits the growth of plants.
Although polycarbonate sheets might entail a higher initial cost compared to other plastics, their extended lifespan and superior durability can ultimately make them a cost-effective choice in the long term. When determining the most appropriate plastic material for your greenhouse, it's essential to consider your specific greenhouse requirements, climate conditions, and budget.
What is hoop house?
A hoop house, also referred to as a high tunnel, is a type of greenhouse structure designed to prolong the growing season and create a sheltered environment for plants. It features a series of arched metal or plastic hoops covered with transparent or translucent plastic film. This uncomplicated yet effective design forms a curved tunnel-like structure that encloses a designated area for cultivation.
Hoop houses are commonly utilized to establish a microclimate that shields plants from unfavorable weather conditions like frost, heavy rain, wind, and extreme temperatures. The plastic covering permits sunlight to enter, generating a greenhouse effect that raises internal temperatures and maintains a more consistent climate compared to the open outdoors.
How long does the plastic greenhouse lasts?
The duration for which a plastic greenhouse remains functional can vary widely, influenced by factors such as plastic quality, climate conditions, maintenance practices, and the specific plastic type used. Typically, a properly cared-for plastic greenhouse can endure anywhere from 5 to 15 years.
Plastics of superior quality, like polycarbonate or more robust versions of UV-protected polyethylene, usually have lengthier lifespans. These materials are engineered to withstand UV rays, temperature fluctuations, and physical stresses arising from wind, snow, and hail.
However, plastics that are cheaper or of lower quality may degrade more swiftly, particularly under intense sunlight and severe weather. They might become brittle, discolored, or prone to tearing, shortening their effective longevity.
Regular maintenance plays a crucial role in extending the life of a plastic greenhouse. Routine cleaning to eliminate dirt, debris, and dust, coupled with inspections for damage and timely repairs, can ensure the plastic remains in optimal condition. The application of shading or reflective coatings can also minimize UV exposure and extend the plastic's lifespan.

 Rated Excellent
Rated Excellent